Acid Saccharides, Phosphorylated Saccharides
Galacturonic acid is one of uronic acids and exists as a one of components of bacterial polysaccharides such as pectin. This chromatomgram shows an anlysis of galacturonic acid oligomers using an Asahipak NH2P-50 4E column with phosphate buffer as the eluent. Oligogalactronic acids, from monomer to hexamer, are separated.
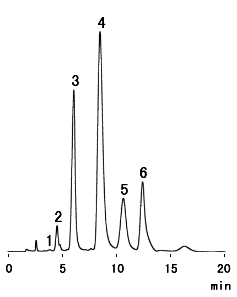
Sample : Oligogalacturonic acids (Courtesy of Dr. Yoshino, Kyoto Women’s University)
1. Galacturonic acid
2. Oligogalacturonic acid dimer
3. Oligogalacturonic acid trimer
4. Oligogalacturonic acid tetramer
5. Oligogalacturonic acid pentamer
6. Oligogalacturonic acid hexamer
Column : Shodex Asahipak NH2P-50 4E (4.6mmID*250mm) Eluent : 0.3M Sodium phosphate buffer(pH4.4) Flow rate : 1.0mL/min Detector : UV(210nm) Column temp. : 40deg-C
Glucose can be anearobically decomposed into lactic acid and ethanol. This decomposing process is called as glucolytic pathway. In this pathway, some products such as glucose-1-phosphate, glucose-6-phosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, etc. are produced as intermediary products. Here, glucose-1-phosphate, fructose-6-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate are analyzed using Asahipak NH2P-50 4E by ion-exchange mode. It was confirmed that the retention is stronger and separation is better by using lower concentration phosphate buffer.
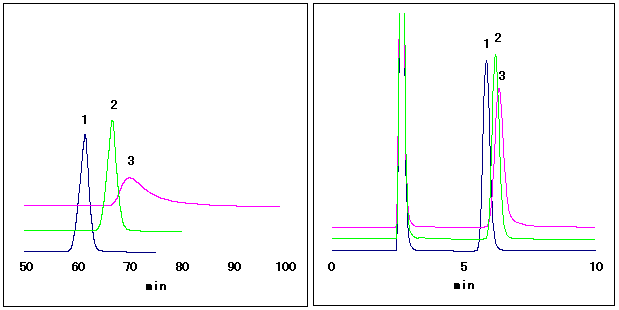
Sample : (Left); 20mg/mL each, (Right); 10mg/mL each, 20micro-L
1. Glucose-1-phosphate
2. Fructose-6-phosphate
3. Glucose-6-phosphate
Column : Shodex Asahipak NH2P-50 4E (4.6mmID*250mm)
Eluent : (Left); 10mM Sodium phosphate buffer(pH4.4)
: (Right); 150mM Sodium phosphate buffer(pH4.4)
Flow rate : 1.0mL/min
Detector : Shodex RI
Column temp. : 40deg-C
Glucose can be anearobically decomposed into lactic acid and ethanol.This decomposing process is called as glucolytic pathway. In this pathway, some products such as glucose-1-phosphate, glucose-6-phosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, etc. are produced as intermediary products. Here, fructose-6-phosphate and fructose-1,6-bisphosphate are analyzed using Asahipak NH2P-50 4E by ion-exchange mode.
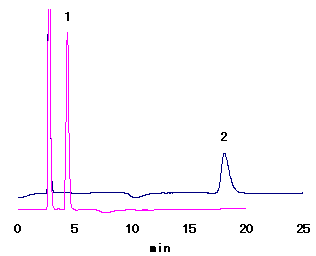
Sample : 5 mg/mL each, 20micro-L
1. Fructose-6-phosphate
2. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Column : Shodex Asahipak NH2P-50 4E (4.6mmID*250mm) Eluent : 300mM Sodium phosphate buffer(pH4.4) Flow rate : 1.0mL/min Detector : Shodex RI Column temp. : 40deg-C
Phytic acid and Sodium phytic acid were analyzed using 2 columns of Asahipak GS-220 HQ. Phytic acid was eluted near exclusion limit of GS-220 HQ.
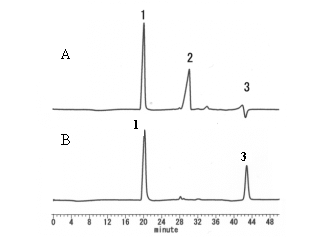
Sample : 20micro-L
A) Phytic acid sodium salt
B) Phytic acid
1. Phytic acid
2. Na+
3. HClO4 -vacant peak
Columns : Shodex Asahipak GS-220 HQ (7.5mmID*300mm) x 2 Eluent : 10mM HClO4 aq. Flow rate : 0.6mL/min Detector : Shodex RI Column temp. : 40deg-C
N-acetylneuraminic acid and N-glycolyneuraminic acid, family of sialic acid, were separated using organic-acids-analysis column, RSpak KC-811.
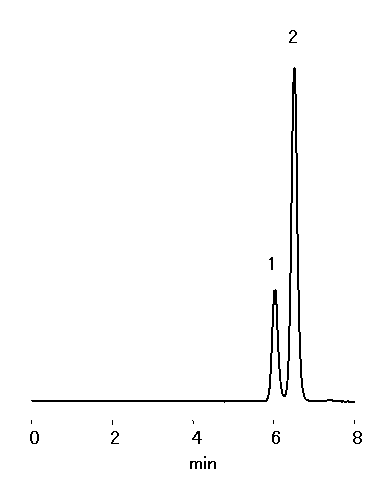
Sample : 0.1% each, 40micro-L
1. N-Glycolylneuraminic acid
2. N-Acetylneuraminic acid
Column : Shodex RSpak KC-811 (8.0mmID*300mm) Eluent : 1% H3P04 aq. Flow rate : 1.0mL/min Detector : UV(210nm) Column temp. : 40deg-C
